British Airways' Bold Imagery Campaign

In their latest marketing campaign, ‘Windows’, British Airways has embraced a minimalist approach. Developed by Uncommon Creative Studio, this campaign features:
-
A focus on curiosity and wonder
-
Capturing the emotions of passengers as they gaze out of an aircraft window
-
A subtle storytelling approach
-
Six British Airways staff
-
Highlighting the brand’s commitment to creating memorable experiences for its customers.
The campaign includes 11 images that showcase the awe and curiosity on passengers’ faces, making viewers ponder what lies beyond the edges of the advertisement. This print nature strategy not only enhances brand awareness but also sparks conversation, proving that sometimes, less is indeed more.
Specsavers' Viral Humor Ad

The internet has been swept up by Specsavers’ humor-driven campaign. Featuring a branded van suspended by a bollard with a red warning sign next to it, this ad has captured the public’s attention and gone viral. The campaign’s success lies in its memorable visual content and the public’s familiarity with Specsavers’ famous tagline.
This ad is a perfect example of how humor can be leveraged to create a lasting impression. By grabbing attention and making people stop and look, similar to how traffic forms opposite a motorway accident, Specsavers has effectively boosted its brand recognition through this clever and humorous approach to ad features.
Rhode Skin's Innovative Product Design
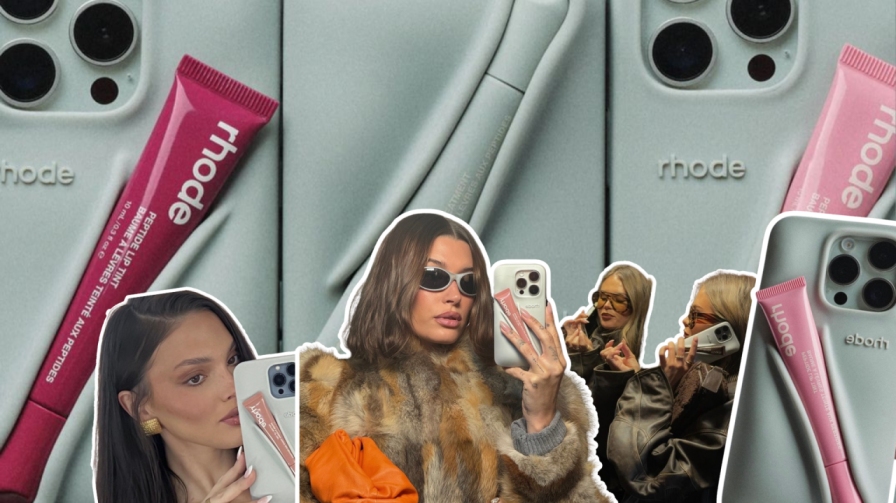

Rhode Skin garnered the market’s attention with the introduction of an innovative product.—a phone case designed to hold lip treatments and tints. This creative and practical design not only ensures that customers always have their lip products on hand but also turns them into walking billboards for the brand. Hailey Bieber, the face and CEO of Rhode Skin, has played a significant role in connecting with consumers through her genuine passion for skincare.
The campaign’s creativity, showcasing the product’s key trait, has even inspired Heinz to develop a similar concept as a joke—a phone case that holds a single packet of ketchup. This playful exchange between brands highlights the impact and originality of Rhode Skin’s marketing strategy.
Tinder's Storytelling Approach

With the power of storytelling, Tinder’s global campaign, ‘It Starts With a Swipe’, strikes a connection with its audience. By showcasing diverse love stories and promoting inclusivity, Tinder has created content that resonates with a wide range of identities and orientations. The campaign intertwines product features with authentic narratives, making the messaging both relatable and engaging.
Innovative features like ‘Share My Date’ and ‘Matchmaker’ have been introduced to enhance user experience and safety. Designed for vertical formats like Instagram TV, this campaign not only promotes Tinder’s new functionalities but also reinforces its commitment to inclusivity and human connection.
Kellogg's Empowerment Initiative

In partnership with cookbook author Molly Baz, Kellogg’s launched a powerful women’s empowerment campaign. This initiative is eye-catching and purpose-driven, featuring Molly Baz with an exposed pregnant belly on a limited edition cereal box. As the first cereal box to feature a pregnant woman, this campaign marks a significant shift in Kellogg’s marketing strategy and aims to inspire and empower women.
The campaign is part of the ‘Special for a Reason’ initiative, which highlights inspiring individuals. By partnering with popular figures like Molly Baz, Kellogg’s hopes to revitalize interest in its cereal products and promote positive messages of empowerment.
MMB's Toaster Swatches for Revolution Cooking

To highlight the precision of their toaster, MMB’s Toaster Swatches campaign for Revolution Cooking cleverly leveraged print ads. The ads feature differently burned toast arranged like color swatches, emphasizing the toaster’s ability to make toast exactly as the user likes it. This creative approach not only captures attention but also effectively communicates the product’s key trait.
By driving inquiries through visually appealing and functional ads, the campaign directs people to purchase from the producer’s web store or retail places, effectively increasing their purchase intent. This clever use of color swatches to represent toast shades has made MMB’s campaign stand out in the market, as the ad drives purchase intent.
McDelivery's "Skip the Dishes" Visuals

The visually striking ads of McDelivery’s ‘Skip the Dishes’ campaign by DDB Prague have captivated audiences. The campaign features dirty dishes forming iconic McDonald’s items like the Big Mac, fries, and a McSundae, highlighting the convenience of McDelivery. This creative visual content emphasizes the message that customers can avoid dirty dishes by opting for McDelivery.
The ad campaigns included three print ads that were both memorable and effective in conveying the convenience of the service. Creative directors Radouane Hadj Moussa and Gert Laubscher have successfully executed a campaign that resonates with consumers and enhances brand awareness.
Discover the Olympics 2024 Marketing.
Nissan’s Artistic Technology Promotion

To promote its innovative high-beam assistant technology and the latest electric vehicle model, the ARIYA, Nissan’s recent marketing campaign skillfully merges traditional Japanese art with modern technology. The campaign uses the car to create real-life zoetrope animation, emulating Shodo calligraphy and reflecting Nissan’s Japanese heritage. This artistic approach makes viewers feel as if they are creating art while driving the ARIYA.
Nissan’s High Beam Assist system, which automatically switches headlights from high to low beam and back, is a key feature highlighted in the campaign. Operating at speeds of approximately 19 mph and above, this system reduces the driving burden and enhances safety. The campaign’s use of traditional art forms to showcase modern technology creates a unique and compelling narrative that stands out in the crowded automotive market.
By featuring the all-electric Nissan ARIYA and its e-4ORCE technology, the campaign not only highlights technological innovation but also underscores Nissan’s commitment to sustainability and heritage.
LEGO City's Kid-Created Epic Story

LEGO City’s marketing campaign, ‘An Epic Story Written by Kids’, engages its target audience through a playful and humorous approach. Produced in collaboration with The LEGO Agency and BETC Paris, the campaign features children as the architects of a humorous action movie set in a bustling metropolis called LEGO City. The narrative is filled with action, humor, and heart, resonating deeply with children.
The campaign video, titled ‘The Robbers Try to Steal the Bank, but Do They?’, highlights children’s imagination and creativity as they play with LEGO sets. By emphasizing timeless lessons such as courage, teamwork, and compassion, LEGO City’s campaign successfully captures the essence of childhood play and adventure.
Pantone’s Surreal “Create Your World”

Inspiring creativity through the use of surreal, otherworldly settings, Pantone’s ‘Create Your World’ campaign stands out. The campaign aims to show that colors are gateways to realms of imagination and creativity, capturing the attention of artists, designers, and the general public. By utilizing both Instagram and print media, Pantone has engaged a broad audience and encouraged them to explore the psychological and emotional impact of color.
Future initiatives of the campaign may delve deeper into how colors can shape our perceptions and emotions, further solidifying Pantone’s role as a leader in color innovation.
Do you need a content marketing agency for your brand? Click Best Content Marketing Agencies to discover.
Amnesty International’s “Pain-Tings”

Amnesty International’s ‘Pain-Tings’ campaign adopts a powerful approach to heighten awareness of domestic violence against women. By altering famous paintings to depict women with bruises and wounds, the campaign highlights the pervasive issue of domestic violence. These striking visuals are designed to provoke thought and encourage viewers to take action.
Campaign cards provided information on how women could seek help through Amnesty International, offering a lifeline to those in need. This impactful campaign not only raises awareness but also provides practical support to victims of domestic violence.
SF Department for Disability and Aging Services' “End Ageism”

Directly tackling negative stereotypes of aging, the ‘End Ageism’ campaign from the SF Department for Disability and Aging Services stands strong. Featuring young faces with older eyes, the campaign personifies traits that never get old, such as:
-
wisdom
-
experience
-
resilience
-
compassion
-
creativity
This creative approach encourages residents to recognize the skills and worth of every individual, regardless of age.
By rejecting negative stereotypes about aging, the campaign emphasizes that we can add an average of 7.5 years to life expectancy, promoting a more inclusive and respectful society.
Foodpanda’s Contactless Delivery Innovation

By introducing contactless delivery during the pandemic, Foodpanda significantly boosted its brand awareness and reputation. By making contactless delivery the default option, Foodpanda ensured safety and convenience for its customers.
This innovative approach not only addressed immediate safety concerns but also positioned Foodpanda as a leader in adapting to new consumer needs during challenging times.
Wirefox Design Agency’s Brand Rebuild

Through a mix of social media campaigns, SEO optimization, and targeted content, Wirefox Design Agency successfully rebuilt its brand. Specializing in:
-
SEO-friendly creative web design
-
UX/UI design
-
Responsive web design
-
Custom web design
Wirefox has tailored solutions that emphasize these areas.
Their efforts have paid off, as they now rank #1 on SERPs for “SEO Company Birmingham”. By providing comprehensive website technical reviews and local SEO services, Wirefox has achieved significant visibility and conversion for its clients.
Tony's Chocolonely’s Organic Growth

The rapid growth of Tony’s Chocolonely in the UK underscores the potency of word-of-mouth marketing. Initially avoiding paid media, the brand relied on earned and organic channels to engage consumers. The campaign was designed for organic social virality, encouraging passersby to take photos and post on social media, which caught the attention of journalists and led to extensive free PR coverage.
Recently, Tony’s Chocolonely has started using paid media to accelerate the spread of its message and reach a larger audience more quickly. This strategic shift highlights the brand’s commitment to expanding its reach while maintaining high-quality interactions with consumers.
Key Takeaways
The best marketing campaigns of 2024 have demonstrated the power of:
-
Humor, as seen in Specsavers’ campaign, can make content more shareable and memorable.
-
Emotional appeal, like that used by Dove, creates strong connections with audiences.
-
Innovation, such as the use of virtual reality by Coca-Cola, can create a unique and immersive experience.
-
Larger messages, like Nike’s campaign featuring Colin Kaepernick, can spark important conversations and resonate with consumers.
These strategies have proven to be effective in capturing audience attention and driving success in marketing campaigns, as well as in developing a strong business model. By implementing tactics that capture attention, your marketing efforts can yield even greater results.
Innovation sets brands apart, as demonstrated by Apple’s shift in narrative with the ‘Think Different’ campaign. Campaigns with a larger message, such as:
-
Nike’s ‘Just Do It,’
-
Coca-Cola’s ‘Open Happiness,’
-
Dove’s ‘Real Beauty,’ transcend their products and connect with broader values. These key elements, combined with user-generated content and personalization, can exponentially increase a campaign’s reach and engagement.
Do you want to learn more about unique marketing strategies? Click Red Bull's Marketing Strategy to discover.
How to Manage a Good Marketing Campaign?

To manage a successful marketing campaign, the following are required:
-
A deep comprehension of the target audience
-
Clear objectives
-
Agile marketing and the ability to pivot for adapting to changes and staying relevant
-
Utilizing video content, especially short-form videos, which offer the highest ROI and effectively capture audience attention through concise messaging, making it one of the best marketing strategies.
Data-informed strategies help optimize campaign performance and ensure that marketing messages resonate with the right audience. Prioritizing customer retention and using AI-driven marketing strategies can enhance competitiveness and efficiency. By focusing on these key areas, marketers can create impactful campaigns that achieve their business objectives.
Click The Best AI Image Generators to discover how AI can contribute to digital marketing strategies.
"Discover the best digital marketing solutions. Explore Edvido's top firms."
Frequently Asked Questions

- What makes a good marketing campaign?
A good marketing campaign involves thorough research and goal-setting to address the target audience's needs and align with business objectives, while also creating unique and authentic content with strong visuals and catchy lines to stand out.
- Why is emotional appeal important in marketing campaigns?
Emotional appeal is important in marketing campaigns because it creates strong connections with audiences, making the content more relatable and engaging leading to increased loyalty and brand awareness.
- How can humor be effectively used in marketing campaigns?
Using humor in marketing campaigns can capture attention and make content more shareable and memorable. It can create a lasting impression and enhance brand recognition.
Do you want to find the best PR company for your brand? Click Best Pr Agencies to discover, see the details of Best Pr Agencies in London.
"Discover the best digital marketing solutions. Explore Edvido's top firms."